XMU Research Team Discovers Broad-Spectrum Neutralizing Antibody Against COIVD-19 Variants
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic, has caused over 200 million confirmed cases and claimed over 4 million lives globally. Vaccination is an important instrument for controlling the circulation of coronaviruses that can provide protection and relieve the disease. However, the emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants have diminished the effectiveness of the approved vaccines and reduced the efficacy of existing antibody cocktail treatment under Emergency Use Authorization. New generations of vaccines and broad-spectrum neutralizing antibody therapeutics that could prevent infection of known and future variants are urgently needed.
After countless experiments, the research team of Professor Xia Ningshao, together with the teams from the Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen and University of California, Los Angeles, discovered two cross-neutralizing antibodies and revealed the neutralizing mechanism that induces the depolymerization of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and the shedding of S1 subunit. The discovery will provide options for passive antibody therapeutics and even active prophylactics and inform the design of pan-sarbecovirus vaccines.
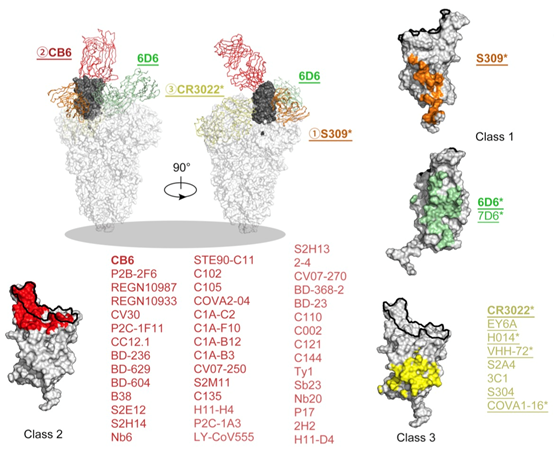
Mutation resistance of 7D6 and 6D6 and comparison of the 7D6/6D6 site with other binding modes of known RBD nAbs
A research paper based on the results titled “Cross-neutralizing antibodies bind a SARS-CoV-2 cryptic site and resist circulating variants” was published on the Nature Communications website on 27 September 2021. Co-first authors of the paper include Postdoc Researcher Li Tingting, PhD student Xue Wenhui and senior engineer Zheng Qingbing from Professor Xia Ningshao’s team, Postdoc Researcher Song Shuo from the Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen, and PhD student Yang Chuanlai and Xiong Hualong from Professor Xia Ningshao’s team. Professor Xia Ningshao, Associate Professor Gu Ying and Professor Li Shaowei from Xiamen University, Researcher Zhang Zheng from the Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen and Professor Zhou Zhenghong from the University of California, Los Angeles are the co-corresponding authors of the paper. The research gained support from National Natural Science Foundation of China, National Key Research and Development Program of China and Xiamen Science and Technology Planning Project.
Paper link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-021-25997-3

